In spoofing hackers’ main goal is to win the trust of the target (Victim) by convincing him that they are interacting with a trusted source. After winning trust, hackers can easily enter the target system, spread the malicious code of the malware, and steal useful information such as passwords, PINs, etc., that the target stores in the system. In spoofing, the hacker’s main objective is to psychologically manipulate the target and win their trust. For example, hackers create a clone of a banking website that completely appears to be legal but when the target enters sensitive information then the whole information is sent to the hacker, which the hacker can use for their own benefit or for other purposes.
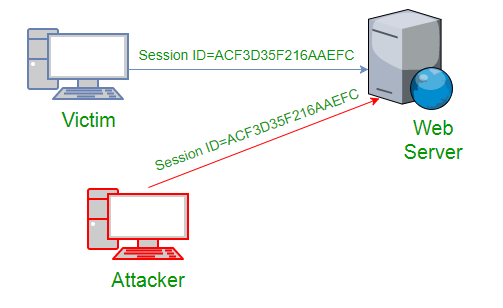
In Hijacking, a hacker can take complete control of a target computer system or hijack a network connection. Once hijacked, the hacker can take control of the target user’s computer system and even easily read and modify the transmitted data or messages. In hijacking, the main goal of a hacker is to take control of a target computer system or network connection to steal information without getting known to the target that they are getting hacked or hijacked. For example, hackers take all the control of the target Computer System and use its camera to gather sensitive information and spy.
Difference Between Spoofing and Hijacking:
Topics to Discuss | Spoofing | Hijacking |
|---|---|---|
Objective | The main objective of hacker in spoofing is to psychologically manipulate the target and win their trust by convincing him. | The main objective of hackers in hijacking is to take control over the target computer system or network connections to steal information without getting known to the target that they are getting hacked or hijacked. |
Requirement | hacker technical Knowledge is required but coding is not that much important. | Technical Knowledge and Coding are Required. |
Software Requirements | The Malicious software needs to be downloaded to the victim’s computer. | Malicious software may or may not be required to download on the victim’s computer. As Hackers, , other security suites do different types of attacks for hijacking. |
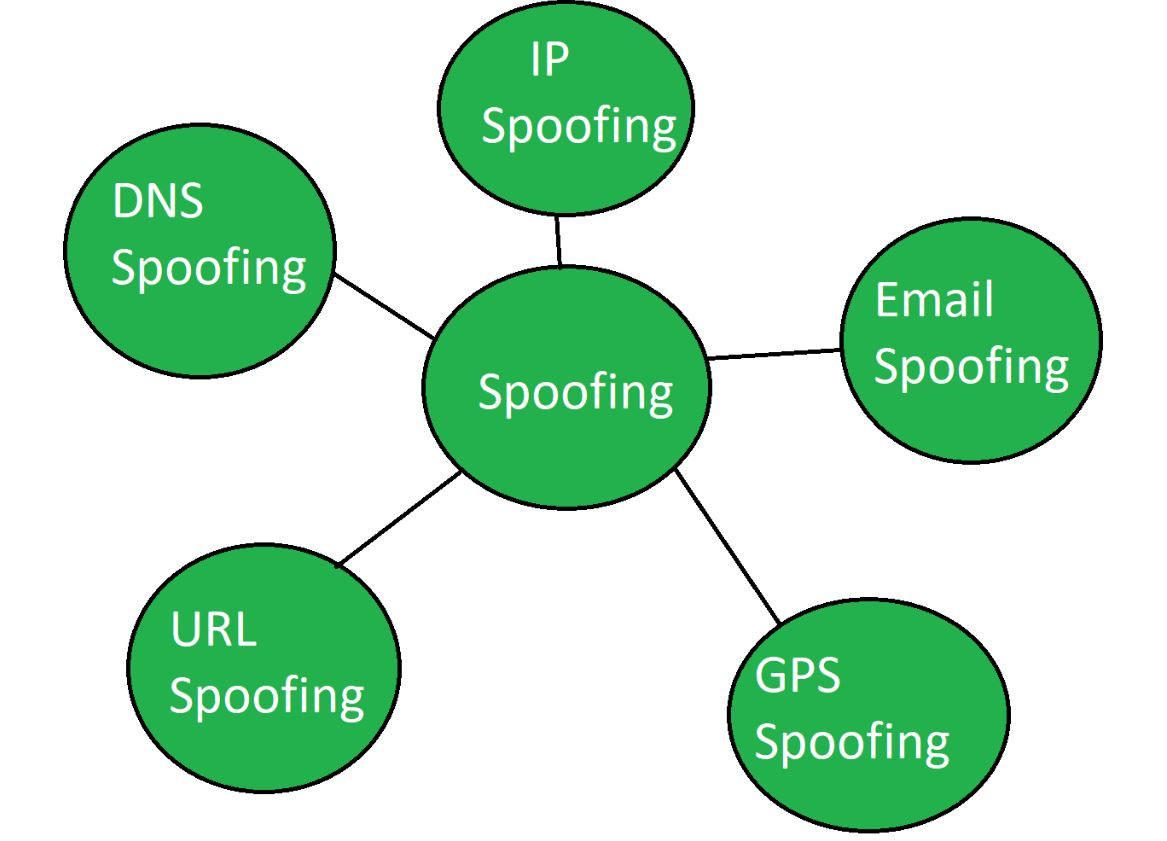
Types | IP Spoofing, Email Spoofing, URL Spoofing etc. | Browser hijacking, session hijacking, domain hijacking, domain name system (DNS) hijacking, Internet Protocol (IP) hijacking, page hijacking etc. |
Preventive Measure |
|
|





 Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖
Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖