IPSec (IP Security) architecture uses two protocols to secure the traffic or data flow. These protocols are ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload) and AH (Authentication Header). IPSec Architecture includes protocols, algorithms, DOI, and Key Management. All these components are very important in order to provide the three main services:
- Confidentiality
- Authentication
- Integrity
IP Security Architecture: 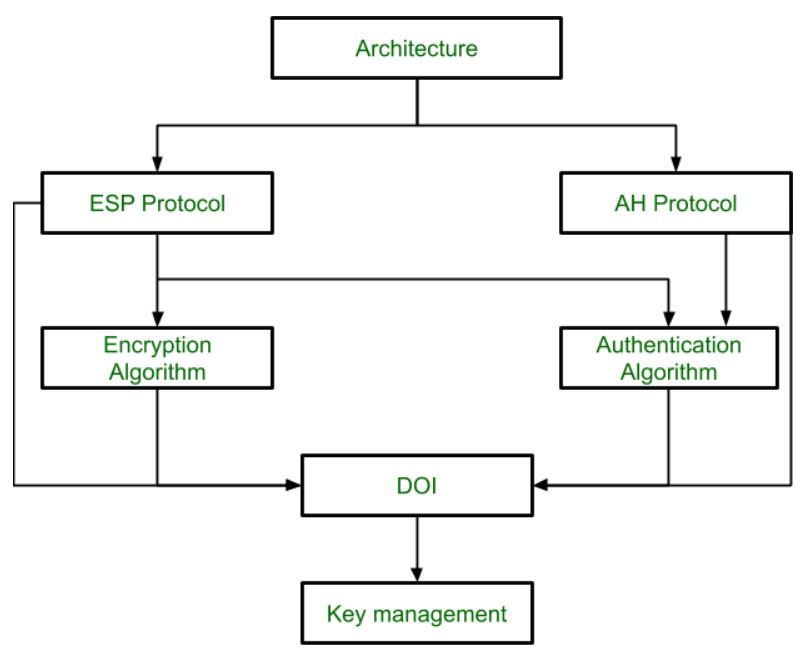
1. Architecture:
Architecture or IP Security Architecture covers the general concepts,
definitions, protocols, algorithms, and security requirements of IP
Security technology.
2. ESP Protocol: ESP(Encapsulation Security Payload) provides a confidentiality service. Encapsulation Security Payload is implemented in either two ways:
- ESP with optional Authentication.
- ESP with Authentication.
Packet Format: 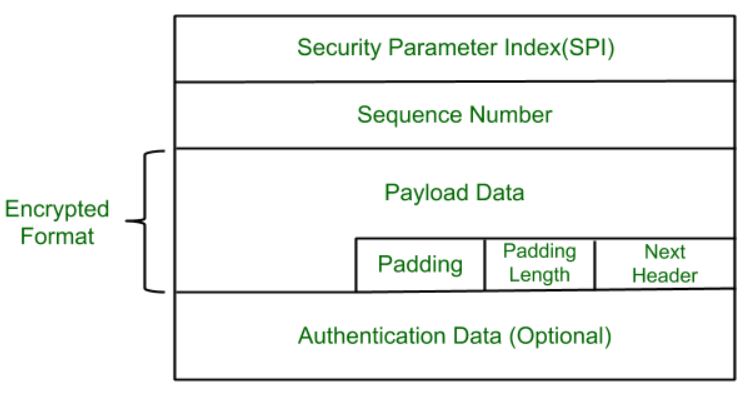
- Security Parameter Index(SPI): This parameter is used by Security Association. It is used to give a unique number to the connection built between the Client and Server.
- Sequence Number: Unique Sequence numbers are allotted to every packet so that on the receiver side packets can be arranged properly.
- Payload Data: Payload data means the actual data or the actual message. The Payload data is in an encrypted format to achieve confidentiality.
- Padding: Extra bits of space are added to the original message in order to ensure confidentiality. Padding length is the size of the added bits of space in the original message.
- Next Header: Next header means the next payload or next actual data.
- Authentication Data This field is optional in ESP protocol packet format.
3. Encryption algorithm: The encryption algorithm is the document that describes various encryption algorithms used for Encapsulation Security Payload.
4. AH Protocol:
AH (Authentication Header) Protocol provides both Authentication and
Integrity service. Authentication Header is implemented in one way only:
Authentication along with Integrity. 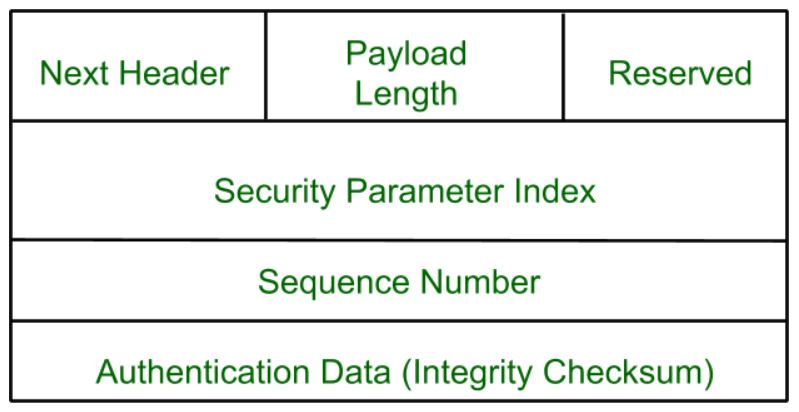
Authentication
Header covers the packet format and general issues related to the use
of AH for packet authentication and integrity.
5. Authentication Algorithm: The authentication Algorithm contains the set of documents that describe the authentication algorithm used for AH and for the authentication option of ESP.
6. DOI (Domain of Interpretation): DOI is the identifier that supports both AH and ESP protocols. It contains values needed for documentation related to each other.
7. Key Management: Key Management contains the document that describes how the keys are exchanged between sender and receiver.





 Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖
Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖