An ethical hacker is able to use a session replay attack with the help of tools like Wireshark or Hping3. The hacker’s goal is to gain access to the network, data, and resources in order to fix any vulnerabilities that can be exploited by adversaries.
Session replay attacks, also known as replay or replay attacks, are network attacks that maliciously “retry” or “delay” valid data transmissions. Hackers can do this by intercepting the session and stealing the user’s unique session ID (stored as either a cookie, URL, or form field). The hacker can now impersonate the authorized user and have full access to do everything the authorized user can do on the website.
A replay attack occurs when a cybercriminal intercepts a secure network communication, intercepts it, and fraudulently delays or transmits it to trick the recipient into doing what the hacker wants. The additional risk of replay attacks is that hackers don’t even need advanced skills to decrypt messages after capturing them from the network. The attack can be successful simply by resending everything.
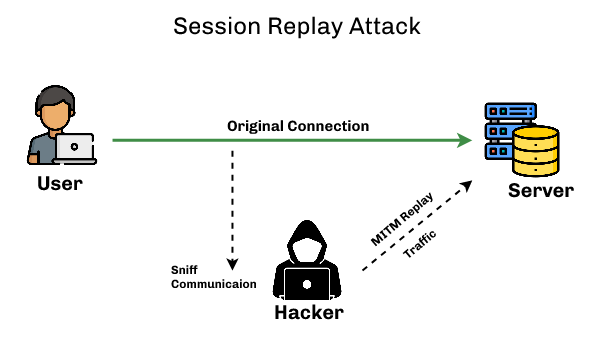
Session Replay Attacks:
A session replay attack is an active intrusion technique where the attacker records and replays a victim’s internet session as if they were an authorized user, thus obtaining credentials for accessing confidential information.
Session Replay Attacks:
A session replay attack is an active intrusion technique where the attacker records and replays a victim’s internet session as if they were an authorized user, thus obtaining credentials for accessing confidential information.
- Your account settings may be hacked without your knowledge if your password can be phished or guessed by brute force.
- The hacker can get access to your network remotely by using tools like BFD, Nmap, or Pivot.
- The attacker’s goal is to gain access to your data by intruding into your system and stealing sensitive information.
Key Points:
- It may be easy for the attacker to know if you are offline or not as they can detect where you are connected from.
- All
the data that the session replay attack captures, is saved and saved in
a format that is easily identified by the hacker, allowing them to take
control of the network remotely.
- The method depends on the type of session replay attack that the hacker is using to hack your account.
- There are many ways for doing a session replay attack.
- To start, the first step that you need to do is find out the IP address of your computer, you can use NMAP (Network Mapper).
- After that, you need to go to your network settings and port forward.
Working:
An attacker can intercept this message, intercept it, and resend it. Since this is just a genuine message that was resent, the message is already properly encrypted and looks legitimate to financial managers. In this scenario, the money manager may respond to this new request unless there is a suspicious reason. This response could consist of sending a large amount of money to the attacker’s bank account.
Example:
The web application holds the session in a query parameter:
A web application can manage a user’s session based on the value of a query parameter,
http://example.com/home/show.php?SESSIONID=MYSESSION, where MYSESSION is the Session ID.
This method is vulnerable to a session-specific replay attack, known as a session fixation attack.
- The attacker generates his own session ID.
- The attacker sends a URL with his session ID to a valid application user.
Eg: http://example.com/home/show.php?SESSIONID=ATTACKER-SESSION
- When a valid user clicks the link, a session will be started with the session ID, ATTACKER_SESSION.
- A valid user connects to the application using his credentials.
- An attacker can now impersonate a valid user by visiting.
http://example.com/home/show.php?SESSIONID=ATTACKER-SESSION





 Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖
Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖