SSH is a secure protocol that can be used to tunnel through firewalls. By using SSH, we can connect to a remote server and tunnel our traffic through the SSH connection. Firewalls
are designed to protect networks from unauthorized access, but a
firewall can also block legitimate traffic if not configured correctly.
This can be a problem when we need to allow access to a specific
application or service. One way to get around this issue is bypassing
the firewall using ssh.
There are a few ways to bypass firewalls using SSH:
- SSH Tunneling: This is the most common way to bypass firewalls. SSH tunneling
creates a secure connection between two hosts over an insecure network.
This connection can be used to tunnel traffic through the firewall.
- SSH Port Forwarding:
This is a less common way to bypass firewalls, but it can be useful in
some cases. SSH port forwarding allows traffic to be forwarded from one
port on the server to another port on the client. This can be used to
bypass firewalls that are blocking traffic on a specific port.
- SSH SOCKS Proxy:
This is another less common way to bypass firewalls. SSH SOCKS proxy
allows traffic to be forwarded through the SSH connection. This can be
used to bypass firewalls that are blocking traffic on a specific port.
Step to Perform SSH Tunneling:
In
order to bypass a firewall using SSH tunneling, we will need to set up
an SSH server on a machine that is outside the firewall. We will then
need to connect to this server using an SSH client and forward traffic
from the client machine to the server machine. For example, let’s say
that we want to bypass a firewall that is blocking all traffic to port
80. We could set up an SSH server on a machine that has port 80 open and
then connect to this server using an SSH client. Once we are connected,
we could then forward traffic from the local machine to port 80 on the
server machine. This would allow us to bypass the firewall and access
websites that are normally blocked.
Now we see setting up a SSH server on a machine that is outside the firewall.
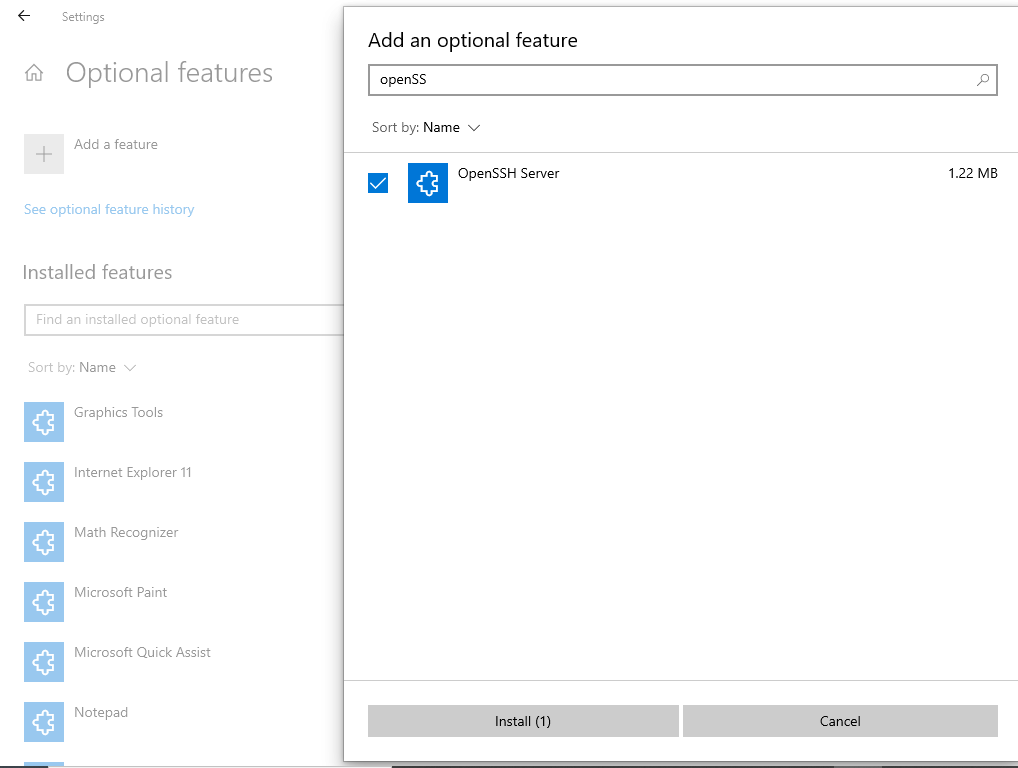
Step 1: Install the SSH server software on the machine.
- On Windows 11:
- Navigate to Settings > Apps > Optional features and click on View features
- Locate “OpenSSH server” feature, select it > check the checkbox, click Next, and then click Install.
- On Windows 10:
- Navigate to Settings > Apps > Apps & features > Optional features and click on Add a feature
- Locate “OpenSSH server” feature, expand the feature > check the checkbox, and select Installation.
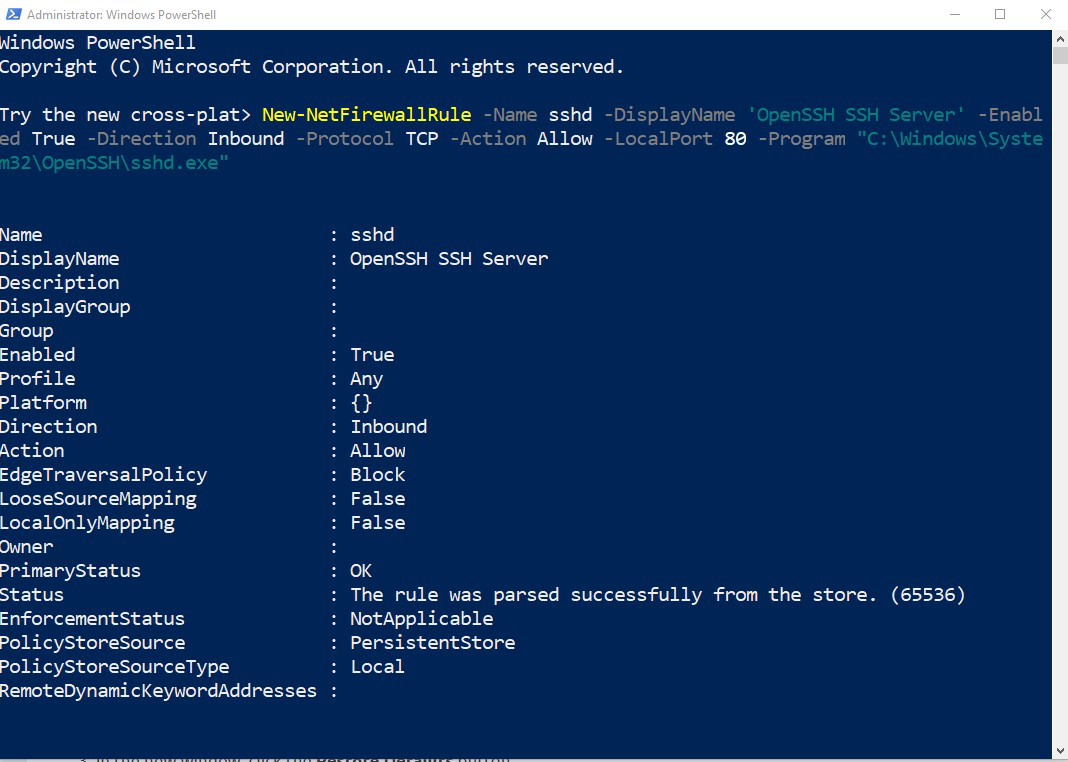
Step 2: Configure the SSH server to listen on port 80 and allow traffic to port 80 through the firewall.
On Windows:
- Navigate
to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender
Firewall1 > Advanced Settings > Inbound Rules and add a new rule
for port 80.
- Or execute the following PowerShell command as the Administrator
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName
'OpenSSH SSH Server' -Enabled True -Direction
Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort
80 -Program "C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\sshd.exe"
Step 3: Start the SSH server
- On
Windows: Navigate to Control Panel > System and Security >
Administrative Tools and open Services. Locate OpenSSH SSH Server
service and click Start the service.
- Once
the SSH server is up and running, and accessible remotely, the next
step is to download an SSH client to the target machine.
Step to Connect the SSH Server and Forward Traffic:
Step 1: Install
the SSH client software on the target machine: The OpenSSH client is
included in Ubuntu Linux distributions by default. There are a few free
SSH clients available for the Windows platform. The best one is Putty,
which is available online on their site.
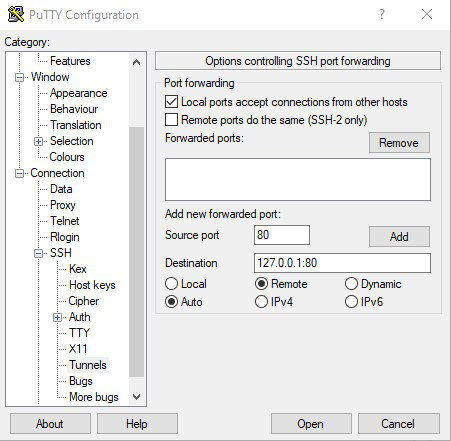
Step 2:
Connect to the SSH server and forward traffic from the target machine
to port 80 on the server machine. After starting Putty, fill in the
following configuration details :
In the “Host Name” field, type the publicly
accessible IP of the SSH server
Navigate to Connection > SSH > Tunnels
Add a new forwarded port:
Source Port = Target Port for Reverse Tunnelling
Destination = 127.0.0.1:[Target Port]
Direction = Remote
Click Add
Click Open to Start the SSH session
At
this point, the target port will be mapped to the target remote SSH
server. This means that clients on the remote network will be able to
access the target PC as if it was on the remote network. Basically, this
creates a private tunnel between two remote end-points, enabling remote
administration of a fire-walled machine.
Perform SSH Port Forwarding:
Assuming
we have SSH access to a remote server, we can use SSH port forwarding
to bypass firewalls. For example, let’s say we want to access a website
that is blocked by a firewall. We can use SSH port forwarding to tunnel
traffic from the local machine to the remote server, and then from the
remote server to the website.
To do
this, we would first SSH into the remote server. Then, we would use the
following command to forward traffic from the local machine (port,
8080) to the remote server (port 80):
ssh -L 8080:localhost:80 user@remote.server.com
Now,
we can access the website by going to http://localhost:8080 in the web
browser. The traffic will be tunneled through the SSH connection, and
the remote server will act as a proxy.
We
can also use SSH port forwarding to tunnel traffic from the remote
server to the local machine. For example, let’s say we want to access a
database that is only accessible from the remote server. We can use SSH
port forwarding to tunnel traffic from the remote server to the local
machine (port 3306) and then connect to the database using the local
machine.
To do this, we would first SSH
into the remote server. Then, we would use the following command to
forward traffic from the remote server (port 3306) to the local machine
(port 3306):
ssh -R 3306:localhost:3306 user@remote.server.com
Now,
we can connect to the database using the local machine. The traffic
will be tunneled through the SSH connection, and the local machine will
act as a proxy.
Perform SSH SOCKS Proxy:
Assuming we have an SSH server running on a remote machine that we can access:
Step 1: On the local machine, open a terminal and run the following command:
ssh -D 9999 -f -C -q -N username@remotemachine
Step 2: This will establish a SOCKS proxy on port 9999 of the local machine.
Step 3: To use the proxy, configure the browser or other application to use a SOCKS proxy on localhost:9999.
Step 4: Browse the web all traffic will be tunneled through the SSH connection.






















 Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖
Hlo guys wellcome to our community its non profit community made for hackers
and we are helping people to know scam and fraud and developing new things of hacking to get up in digital world 🌎 so let’s start 🎖